Scenario: You just had an idea and need an API to communicate your front-end or mobile app to a database. In order to do so you look for a cloud solution for both the database and the server to host your API.
If you’ve already been in this situation you know that it is not cheap. Cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) usually give you a period of time to test technologies. Nevertheless, you have to pay for it when the free period ends or you exceed use.
Even when you want to publish a small project, it is hard to find a good cost-benefit solution. For example, you could host the API on an AWS EC2 instance and use RDS to store your data. However, not only would you have a fixed cost for the instances but it also wouldn’t have autoscaling or high availability features unless you put it behind a load balancer, which would increase the costs even more. Additionally, you have AWS RDS costs that are not less than $20 a month for a t2.micro MySQL (5GB magnetic storage).
Using these three services, API Gateway + Lambda + DynamoDB, you have a serverless, autoscaling, highly available and considerably cheaper solution, not to mention that if you don’t use it you don’t have to pay anything!
In this article I’ll guide you on how to build a CRUD API using .net Core. I’ll try to be as straightforward as possible to save you time. Nevertheless, let’s remember what those three services are:
API Gateway – It is a fully managed service that makes it easy for developers to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale. Basically, it allows you to create REST API to call lambda functions, applications, backend services and so on.
Lambda – For those who work with Azure, it is similar to Azure Functions. AWS Lambda allows you to run code without provisioning servers. In other words, it is a serverless service. You pay only for the compute time you consume. That is one reason we chose this for our solution.
DynamoDB – Key-value and document database. It’s similar to CosmosDB in Azure. It is a NoSQL database, very fast, with multi-region replication feature, serverless, with high availability and fault tolerance. For further details and informations go to: https://aws.amazon.com/dynamodb
CloudFormation – It is a service that allows you to provision all resources you need for your infrastructure in the cloud. Basically, you can write a script that creates new instances, S3 Bucket, DynamoDB table, load balancers (ELB), etc.
Getting hands dirty
First thing, it is faster to use the command-line (terminal). If you are not familiar with it, it’s worth getting used to it.
This command installs Lambda templates for .NET, so if you haven’t installed it yet, run the following command:
dotnet new -i Amazon.Lambda.Templates
Then run the following command. serverless.DynamoDBBlogAPI is the name of template and MyCheapestApi is the name of the project, you can change the value of the -n parameter
dotnet new serverless.DynamoDBBlogAPI -n MyCheapestApi
The command above creates two projects. The BlogPosts CRUD operation project and a Test project. Add them to a new solution:
cd MyCheapestApi
dotnet new sln -n MyCheapestApi\
dotnet sln MyCheapestApi.sln add */*/*.csproj
At this point you should have AWS Credentials configured. If it’s not, please click here first and follow the steps to set it up.
If you navigate to test folder you can run the test. The test class creates a dynamoDb table, executes CRUD operations and deletes the table using US-West (Oregon) region by default.
cd test/MyCheapestApi.Tests/
dotnet test
Inside src folder there’s a file called serverless.template. This is an AWS CloudFormation template file that declares the resources will be created when deploying the application. In this case, a DynamoDB table, an API Gateway to expose the lambda functions (1 for each CRUD operation) and the functions themselves.
dotnet tool install -g Amazon.Lambda.Tools If it is already installed, run this command to check if you are working with the latest version:
dotnet tool update -g Amazon.Lambda.ToolsLet’s see the C# code generated:
As we can see, it automatically generates methods for CRUD operations except for UPDATE (Add, Remove, get by Id and get first result page from scanning operation, something like GetAllBlogPosts)
If you take a look at the serverless.template file you will see all the resources are going to be provisioned when you deploy the project. Notice that if you intend to modify the project to use a class (Entity) you already have, don’t forget to change the content of these files with the proper entity name.
It’s also possible to create a DynamoDB table from the AWS console and delete the lines related to table creation.
Publishing
Now you can deploy your API using the following command:
dotnet lambda deploy-serverless -t serverless.template -sb mycheapestapi -sn MyCheapestApi To start making requests to your new API go first to the AWS Console, API Gateway menu, select the stage (Prod for example) and check the url:
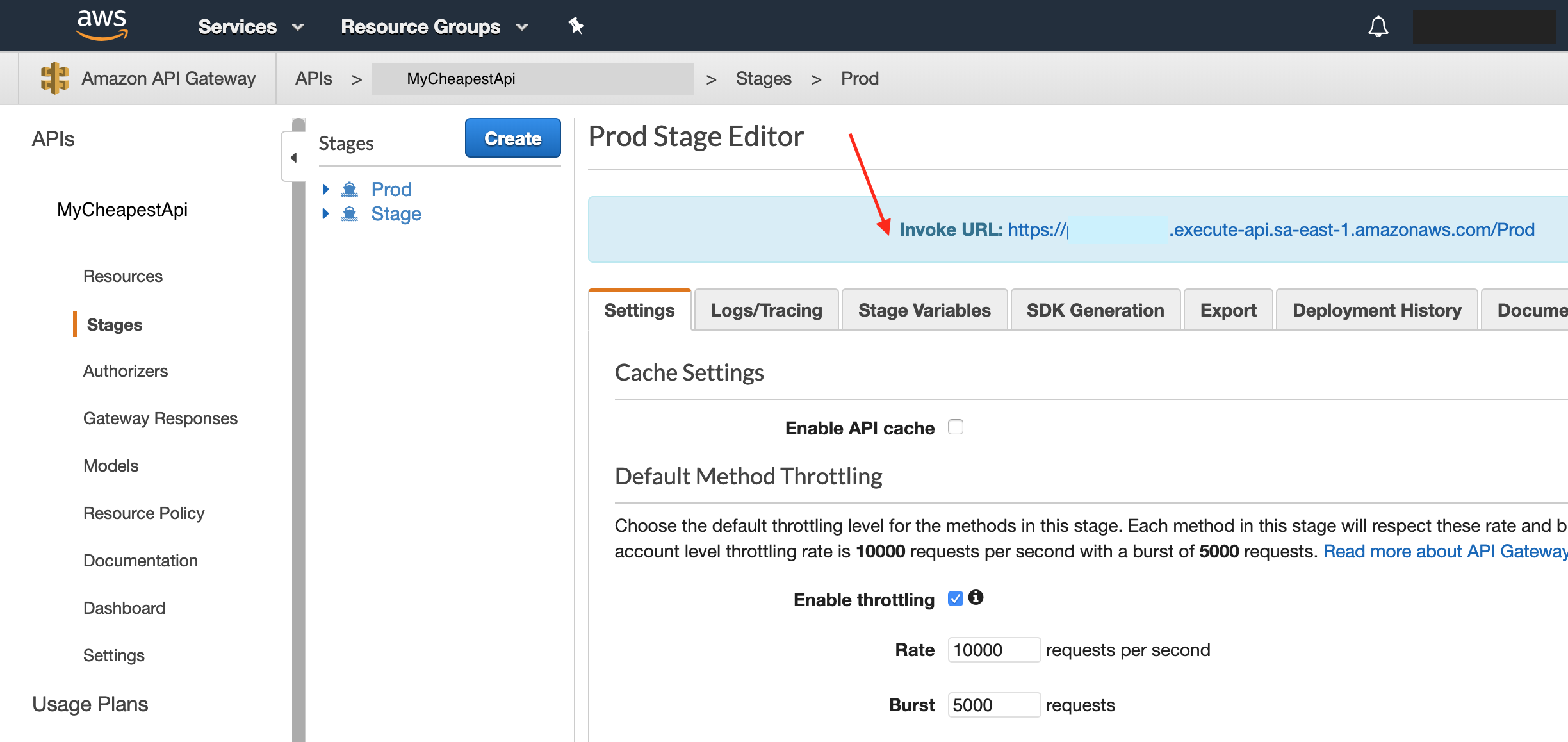
Conclusion
As we can see, this is an amazing low cost solution specially if you don’t want monthly commitment costs in your project, even when your API gets no requests. There are many other good solutions. However I’d like to show you something fast to build which you can start using without worrying whether it fits into your budget. Please fell free to contact me if you have any question or comment.
